Pain relief is a common concern for many individuals, and over-the-counter (OTC) medications like Aleve vs Advil often come to mind. Both are effective in addressing various types of pain, but their differences can impact how and when they are best used. In this article, we will explore the similarities, differences, and specific uses of Aleve vs. Advil to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Aleve vs Advil
What is Aleve?
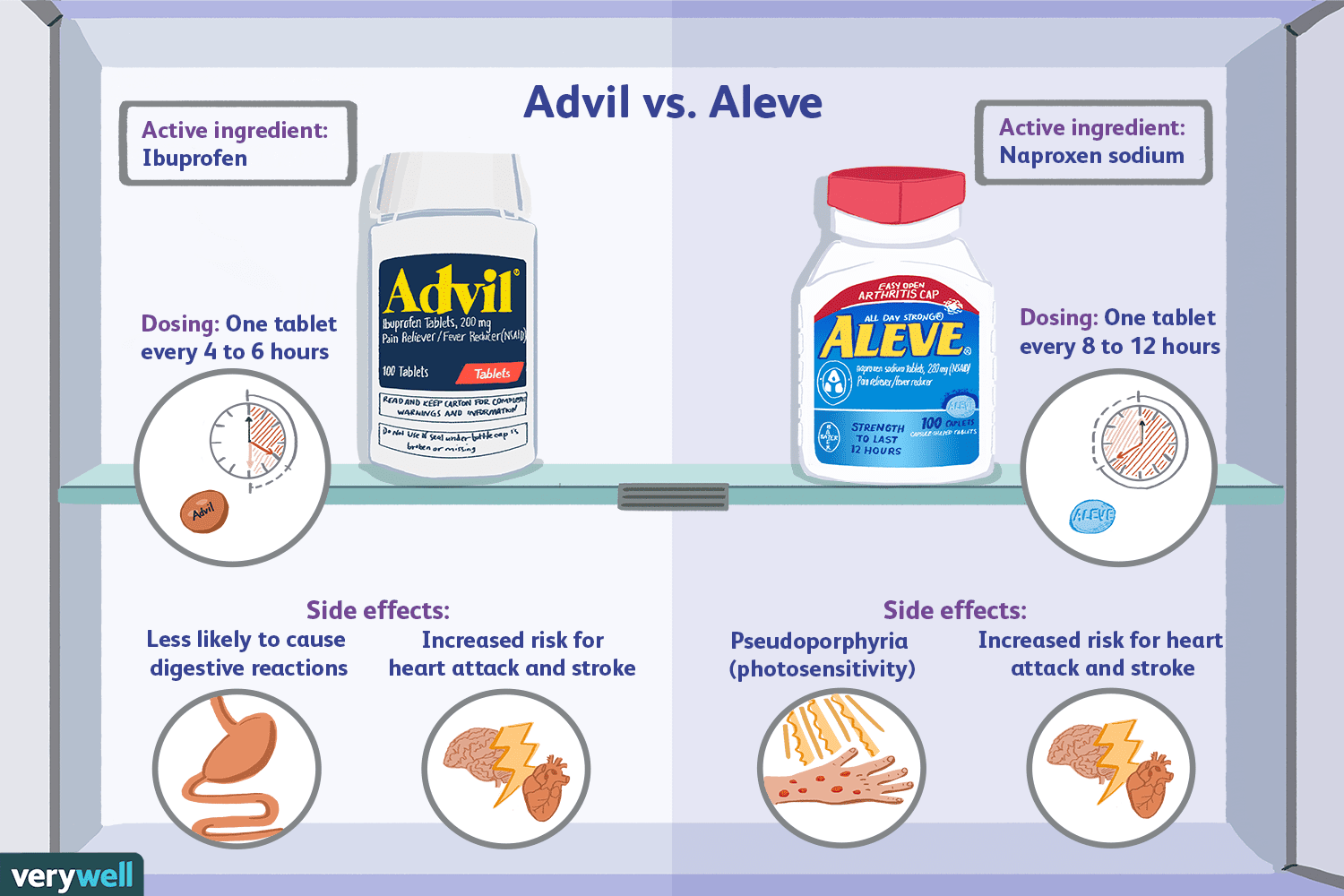
Aleve, a brand name for naproxen sodium, is an NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) commonly used to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever. Due to its extended duration of action, Aleve is particularly effective for longer-lasting pain relief, making it suitable for conditions like arthritis and menstrual cramps.
What is Advil?
Advil, a brand name for ibuprofen, is also an NSAID. It is widely recognized for reducing pain, inflammation, and fever. Advil is known for its rapid onset of action, providing quicker relief for acute pain such as headaches, toothaches, or minor injuries.
Similarities Between Aleve vs Advil
Both Aleve vs Advil belong to the NSAID class of medications and share some key similarities:
- Pain Relief: Both are effective at reducing mild to moderate pain.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: They help reduce inflammation associated with conditions like arthritis.
- Fever Reduction: Both can lower body temperature Advil vs Aleve in cases of fever.
- Over-the-Counter Availability: Available without a prescription for general pain management.
Key Differences Between Aleve vs Advil
Active Ingredients
- Aleve: Contains naproxen sodium.
- Advil: Contains ibuprofen.
Duration of Action
- Aleve: Typically provides pain relief for 8 to 12 hours, requiring fewer daily doses.
- Advil: Works for 4 to 6 hours, often necessitating more frequent dosing.
Onset of Action
- Aleve: It may take slightly longer to begin working compared to Advil.
- Advil: Offers quicker relief, making it ideal for acute pain.
Dosage and Frequency
- Aleve: The recommended dose is one tablet every 8 to 12 hours.
- Advil: Typically taken every 4 to 6 hours, depending on the severity of pain.
Side Effects
- Aleve: May have a higher risk of gastrointestinal issues, especially with prolonged use.
- Advil: Associated with stomach upset but generally considered gentler on the stomach for short-term use.
Specific Uses
- Aleve: Preferred for chronic conditions like arthritis due to its extended duration.
- Advil: Ideal for acute pain scenarios like headaches or muscle strains.
Aleve vs. Advil: Which Should You Choose?
The choice between Aleve vs Advil depends on several factors, including the type and duration of pain, personal medical history, and potential side effects.
When to Use Aleve
- Chronic pain conditions such as arthritis.
- Situations requiring long-lasting relief.
- Menstrual cramps.
When to Use Advil
- Acute pain such as headaches or toothaches.
- Minor injuries or muscle strains.
- Fever reduction during colds or flu.
Safety and Precautions
General Safety Guidelines
- Avoid combining Aleve vs Advil without consulting a healthcare provider.
- Take with food or milk to minimize stomach irritation.
- Stay hydrated while using NSAIDs.
Who Should Avoid NSAIDs?
Individuals with the following conditions should consult their doctor before using Aleve or Advil:
- Stomach ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Kidney or liver issues.
- Heart disease or high blood pressure.
Aleve vs. Advil for Specific Conditions
Arthritis
- Aleve is often recommended due to its prolonged effect, reducing the need for frequent dosing.
- Advil can also be effective but may require more frequent administration.
Headaches and Migraines
- Advil is typically favored for its faster onset of action.
- Aleve may be a good alternative for longer-lasting headache relief.
Fever
- Both Aleve vs Advil are effective in lowering fever, though Advil’s quicker action makes it a preferred choice for immediate relief.
Menstrual Cramps
- Aleve’s longer duration often makes it a better option for managing menstrual pain throughout the day.
- Advil can be used for immediate relief.
Comparing Side Effects
Common Side Effects
- Aleve: Nausea, heartburn, dizziness.
- Advil: Upset stomach, mild rash, headache.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
- Aleve: Increased risk of cardiovascular issues with prolonged use.
- Advil: Kidney damage with excessive use.
Mitigating Side Effects
- Always follow recommended dosages.
- Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible.
- Consult a healthcare provider if side effects persist or worsen.
Drug Interactions
Both Aleve vs Advil can interact with other medications, such as:
- Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin).
- Blood pressure medications.
- Certain antidepressants.
Always inform your healthcare provider about your medications to avoid potential interactions.
Natural Alternatives to NSAIDs
For individuals seeking non-medication options for pain relief, the following alternatives may be considered:
- Hot and cold therapy.
- Gentle exercises like yoga or stretching.
- Herbal remedies, such as turmeric or ginger.
- Acupuncture or massage therapy.
Conclusion
When compared, Aleve vs. Advil offer effective pain relief but cater to different needs and scenarios. Aleve is ideal for long-lasting Advil vs Aleve relief from chronic pain conditions, while Advil excels in providing quick relief for acute pain. Understanding their differences, benefits, and potential side effects can help you choose which medication to use.
As always, please consult a healthcare professional before starting or switching pain medications to ensure they align with your health needs and medical history. With proper use, Aleve vs Advil can significantly improve quality of life by alleviating pain and discomfort.